What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?
What Is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Click The Image To Discover An All Natural Approach To Neuropathy
Click The Image To Discover An All Natural Approach To Neuropathy
The definition of neuropathy is disease or damage to a nerve or a group of nerves. Before we discuss what is neuropathy, it is important do understand that there are two major classifications of neuropathy: Central neuropathy and Peripheral neuropathy. Both types of neuropathy involve nerve damage. Most people are referring to peripheral neuropathy when using the term neuropathy.
Peripheral neuropathy is damaged or diseased nerves that exists outside of the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord. All other nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord are peripheral (at the edge or outside) hence the term peripheral nervous system. Peripheral neuropathy affects motors function, sensory function and autonomic functions. These three types of peripheral neuropathies all involve nerve damage and will be discussed in detail. Central neuropathy is disease to the nerves of the spinal cord and brain. Neurological disorders such as Parkinson's Disease, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy constitute central neuropathies. Central neuropathy will not be discussed in this article.
Sensory, Motor, and Autonomic Nerves
The peripheral nervous system sends information from the central nervous system to the remainder of the body for motor function. These nerves allow our brain to send signals to our muscles to coordinate movement. These peripheral nerves are called motor nerves.
The peripheral sensory nerves also sends sensory or incoming signals to the central nervous system. These nerves allow our brain to process the electrical signals dealing with touch, position, and vibration. These peripheral nerves are called sensory nerves.
There is a third category of peripheral nerves known as the autonomic nerves. These nerves allow the brain to regulate bodily functions that are not completely under voluntary control. Examples of these bodily functions include the heart rate, bladder control, and the digestive process.
These nerves -- sensory, motor, and autonomic -- make up the peripheral nervous system.
The Nerves Outside Of The Brain And Spinal
Cord Make Up The Peripheral Nervous System
The Nerves Outside Of The Brain And Spinal
Cord Make Up The Peripheral Nervous System
Causes Of Peripheral Neuropathy
There are variety of causes of peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral nerves can be damaged from trauma, infections, metabolic abnormalities, and toxins (poisons). Some of these toxins include drugs to treat cancer. Peripheral neuropathy may be mild but sometimes, the nerve damage can be severe. It's difficult to predict the severity of disease as peripheral neuropathy varies from individual to individual. The are certain autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis that can also cause peripheral neuropathy. There is an association of chronic liver disease and peripheral neuropathy. Certain infections and vaccines can trigger the immune system to cause inflammation response to cause peripheral nerve damage that can result in potentially serious complications and even death. One such example is Guillain-Barré syndrome, which is often in response to an infection. Another example is chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy which is similar to Guillain-Barré syndrome. While peripheral neuropathy may have several causes, peripheral neuropathy always results in nerve damage.
An example of a traumatic peripheral neuropathy is carpal tunnel syndrome which there is physical injury to a single nerve in the wrist as a result of repetitive micro-trauma from a repetitive motion. It can be treated in a number of ways such as rest, steroid injections, and surgery.
Examples of a toxic exposure that causes peripheral neuropathy is exposure to lead, mercury, or arsenic.
An example of the an infectious cause of peripheral neuropathy is
shingles which is a reactivation of the herpes zoster virus, otherwise known as the chickenpox virus. The virus reactivates in the peripheral nervous system often resulting in a painful rash within a given nerve area
A Nutritional Deficiency In Vitamin B12 Can Cause Neuropathy.
A Nutritional Deficiency In Vitamin B12 Can Cause Neuropathy.
An example of neuropathy from a metabolic deficiency are vitamin deficiencies. One of the more common vitamin deficiencies is a lack of vitamin B12 also known as cobalamin.
But most common cause of neuropathy is diabetes. Diabetes is the inability to regulate blood sugar levels secondary to abnormalities of insulin. High blood sugar levels can affect nerves and cause damage to the small blood vessels known as capillaries which supply oxygen and blood to our small nerves. As a result of this damage, nerve function is impaired leading to peripheral neuropathy, otherwise known as diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy cannot be reversed. It results in permanent nerve damage. Getting regular blood tests to monitor blood sugar is of paramount importance to minimize any damage.
Discover An All Natural Approach To Neuropathy
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
1. Peripheral Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy usually affects the feet and legs, but it can also affect the arms or hands. Symptoms are varied and can be mild to severe. They include:
-numbness (sensory neuropathy)
-tingling or burning sensations (early symptoms)
-shooting pain or a sharp pain
-extreme sensitivity to touch causing severe pain
-insensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
-cramping
-muscle weakness (motor neuropathy)
-loss of coordination making it difficult to control movement and causing difficulty walking
Some people feel pain more often at night, and each these symptoms can be a significant diabetes complication affecting the quality of life. There can be severe shooting pains, sharp pains, and chronic pain from the nerve damage. These pains has been known to lead to depression and even suicide in people with diabetes.
If you have diabetic peripheral neuropathy, you may not feel an injury or sores on your foot. Moreover, damage to the small blood vessels in your feet from a high blood sugar contributes to poor blood flow and poor wound healing. This nerve tissue damage is one of the main reasons for foot problems and infections and the subsequent need for amputation in diabetics. This is a common complication which can be mitigated or avoided by an early diagnosis. Diabetics must check their feet on a daily basis and care for wounds immediately to prevent the development of a foot ulcer and the need for amputations.
Diabetics Must Check Their Feet Everyday
For Minor Cuts And Other Wounds.
Diabetics Must Check Their Feet Everyday
For Minor Cuts And Other Wounds.
2. Autonomic Diabetic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy is the second most common type of diabetic neuropathy next to peripheral neuropathy.
As mentioned earlier, the autonomic nervous system is part of the peripheral nervous system and regulates other systems in your body over which you do not have complete conscious control. These body systems include your digestive system, cardiovascular system including the control of blood pressure, bladder and sexual organs, and your ability to sweat. The complications diabetic neuropathy causes from an autonomic perspective include low blood pressures, dizziness, fainting episodes, and a labile heart rate. A blood pressure that is too low can cause fainting.
Digestion Problems From Autonomic Diabetic Neuropathy
Nerve damage to the digestive tract can manifest as:
-nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and subsequent dehydration
-constipation from slow movement of the intestines
-dysphagia, which is difficulty swallowing
-gastroparesis, which is the inability of the stomach to undergo peristalsis (involuntary contractions followed by periods of relaxation) to propagate food from the stomach into the intestines. Gastroparesis can cause early satiety ( the sensation of being full after only a few bites) that can result in extreme weight loss. Gastroparesis can also results in intractable nausea and vomiting.
To make matters even worse, the cumulative effect of these digestive system symptoms can make it all the more difficult to control and manage one's blood sugar often resulting in dangerously high blood sugar levels. Obtaining adequate nutrition is also problematic. Blood glucose monitoring is of vital importance when experiencing this type of neuropathy as it is so easy for the blood sugar to get out of control.
Sweating Problems From Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
Also, symptoms such as sweating and heart palpitations, can go undetected in people with autonomic diabetic neuropathy. This can mean not noticing when you have low blood sugar (hypoglycemia unawareness) or a high blood sugar as these symptoms are often present with perspiration. This is why blood sugar levels must be monitored closely. Furthermore, the impaired sweat glands can make it difficult to regulate a normal body temperature.
Sex Organs And Bladder Problems From Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
Cardiovascular Problems From Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy
Damage to the nerves that control your heart rate and blood pressure can make them respond more slowly. These are examples of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. You may experience a drop in blood pressure making you feel light-headed or dizzy when you stand up after sitting or lying down. These low blood pressure symptoms can also occur with simple exertion such as walking, carrying groceries, and climbing up stairs. Autonomic neuropathy can also cause an abnormally fast heart rate.
Autonomic neuropathy can make it difficult to identify some of the symptoms of a heart attack such as chest pain and cold sweats. You may not feel any chest pain when your heart isn't getting enough oxygen. This is particularly relevant as diabetes is of the most important risk factors in heart disease.
3. Proximal Diabetic Neuropathy
4. Focal Diabetic Neuropathy
How Diabetes Causes Neuropathy
Regulating Blood Sugar Levels Is Of Paramount
Importance In Mitigating Diabetic Neuropathy
Regulating Blood Sugar Levels Is Of Paramount
Importance In Mitigating Diabetic Neuropathy
Prevention of Diabetic Neuropathy
This Discovery Can Change The Approach To Neuropathy
Symptoms Of Peripheral Neuropathy, With Or Without Diabetes
Symptoms Of Peripheral Neuropathy, With Or Without Diabetes
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy are typically muscle weakness and pain. The early symptoms often include numbness and tingling. The pain, otherwise known as neuropathic pain, is typically described as stabbing, stinging, burning. In some situations, symptoms improve, especially if they are caused by an illness that is treatable such as a vitamin or mineral deficiency. Sometimes, however, the nerve damage is permanent, and the resulting peripheral neuropathy symptoms can only be controlled and not cured. Doctors may use a muscle and nerve ultrasound machine to assess damage to the muscle and nerve tissue. A nerve biopsy is sometimes used to diagnose peripheral neuropathy if the nerve injury can't be detected by other means. It is important to get peripheral neuropathy diagnosed by a physician.
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment
There are a variety of techniques used that can be fine tuned to treating peripheral neuropathy treatment. The particular treatment depends on the type of nerves affected.
Pain Medications Used To Treat Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms
The Difference Between Non-steroidal Anti-Inflammatory drugs and Narcotics.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) reduce pain by inhibiting enzymes involved in the inflammatory process, in particular an enzyme known as the COX enzyme. Narcotics reduce pain by attaching themselves to certain pain receptors in the brain thereby blocking pain signals to the brain. Narcotics (opioids) do not inhibit inflammation. It is not uncommon for people to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and narcotics as the same time as part of a pain control regimen. They typically do not potentiate each other. You typically don't have to worry about respiratory depression by mixing an NSAIDs and an opioid medication. However, each medical class still retains their respective side effect profile.
The Uniqueness Of Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is not an anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen even though acetaminophen shares the ability to bring down a fever.. Acetaminophen is not a narcotic either even though it shares the organ of function (the brain). Narcotics will not treat a fever like acetaminophen. Acetaminophen will not treat inflammation even though it will treat a fever. It is in its own unique category. Acetaminophen will not cause respiratory depression, and is not known to cause kidney damage of peptic ulcers like NSAIDS. Acetaminophen, however, is know to be specifically toxic to the liver when taken in higher than suggested doses. Finally, it is not uncommon for acetaminophen to be combined with narcotics ( like Tylenol with codeine, or Percocet which is oxycodone with acetaminophen) for pain control. This combination is indeed safe and effective for pain control.
The Active Ingredient In Tylenol Is Acetaminophen.
Acetaminophen Is Not An Anti-Inflammatory Or Opioid.
The Active Ingredient In
Tylenol Is Acetaminophen.
Acetaminophen Is Not An Anti-Inflammatory Or Opioid.
The bottom line with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, narcotics, and acetaminophen is that they decrease the pain felt with peripheral neuropathy but they don't treat the underlying condition. They won't repair the peripheral nerves. The peripheral nervous system is still diseased or damaged.
Other Medications Used To Treat Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms
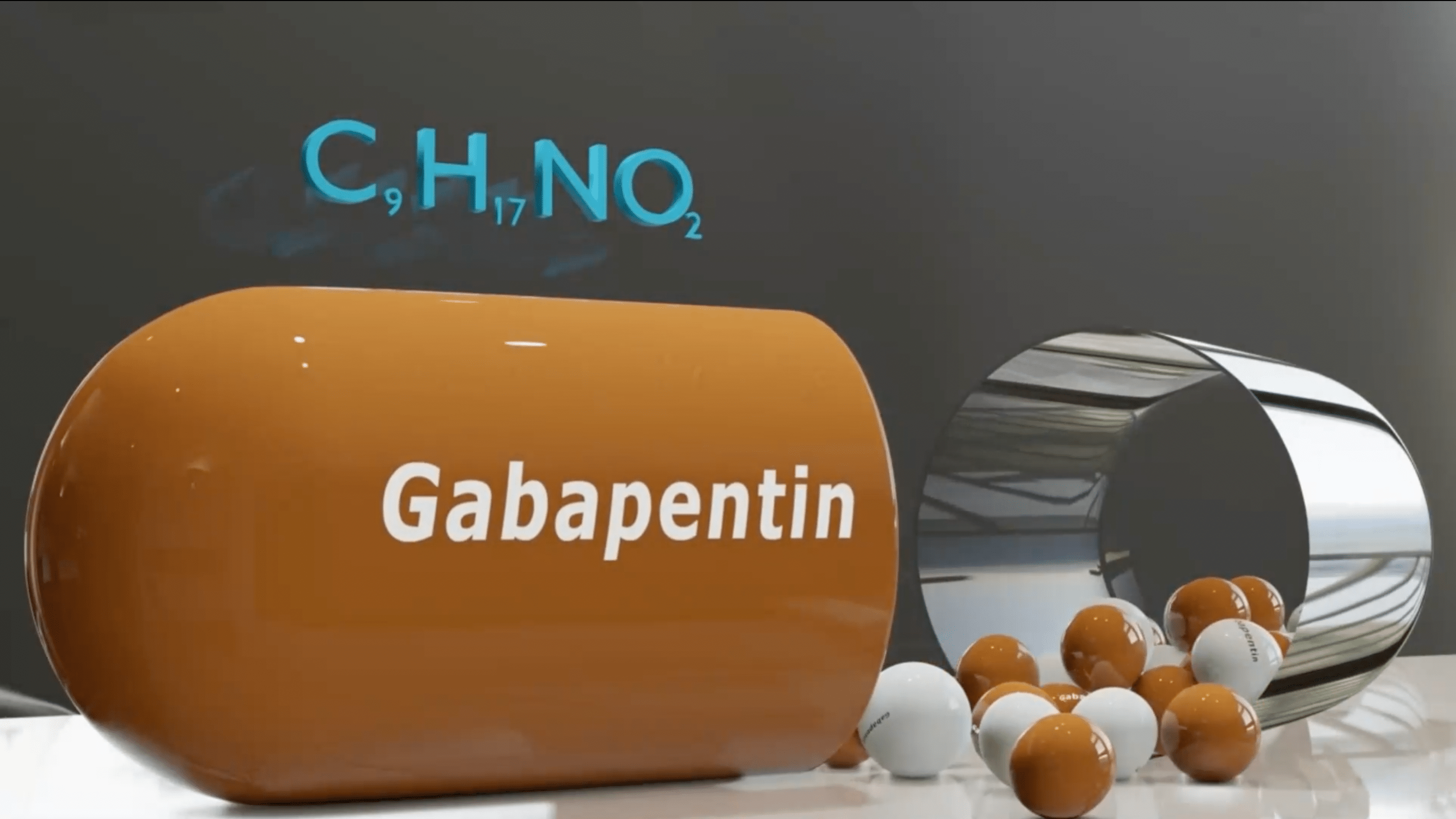
Some antidepressants and anticonvulsants may also be useful in treating the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy even though they also have effects in the central nervous system to treat other neurological diseases. You do not need to be depressed or have seizures to experience relief from neuropathic pain with these medications. They can be quite effective in controlling sensory neuropathy symptoms. Some of these medicines include amitriptyline, gabapentin, carbamazepine (Tegretol) and lamotrigine (Lamictal). These medications are known to interfere with the way pain is transmitted in nerve cells, and are commonly referred to as neuropathic pain agents.
The Gabapentin Market Share Is Over 1.5 Billion US Dollars
Gabapentin For Neuropathic Pain

Eating An Anti-Inflammatory Diet Is Part
Of An Alternative Approach To Neuropathy
Eating An Anti-Inflammatory Diet Is Part
Of An Alternative
Approach To Neuropathy
Dietary and Lifestyle Practices To Treat Peripheral Neuropathy
Certain vitamin deficiencies (such as B-12 deficiency) can contribute to peripheral neuropathy. A diet consisting of whole unprocessed grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can prevent further nerve damage and limit the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Additionally, a healthy diet improves the body's overall functionality. Keeping your blood sugar in a healthy range will definitely help with peripheral neuropathy. Blood tests should be checked on a regular basis.
Additionally, regular exercise is beneficial for maintaining a healthy weight, regulating blood sugar, and preserving muscle strength. However, consult your physician before beginning a new exercise regimen, especially if you suffer from peripheral neuropathy. Even a light exercise regimen of walking can improve symptoms of peripheral neuropathy.
Additionally, tobacco products and excessive alcohol consumption likely contribute to nerve damage and peripheral neuropathy. While quitting smoking is difficult, there are numerous programs and medications available to assist with withdrawal symptoms. Alcohol should be consumed no more than one to two times per day and even this may be too much for certain individuals.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) In Treating Peripheral Neuropathy
When using a TENS machine to treat peripheral neuropathy, special stickers (electrodes) that you adhere to your skin deliver electrical impulses to the affected area of your body. These machines can be used at home and are available over the counter. Electrical impulses are frequently experienced as a tingling sensation and muscle twitches. Electrical impulses can inhibit the transmission of pain signals from multiple nerves to the spinal cord and brain, thereby relieving pain and relaxing muscles.
TENS however is not effective for everyone. It may be unpleasant, but it should not be painful. There may be skin irritation where the electrodes are adhered. TENS cannot be used in the shower or bath.
TENS: Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
A TENS unit allows the user to manage pain for a variety of durations. Typically, the duration of pain relief ranges from 5 minutes to 24 hours. Generally, the level of pain relief will vary based on the nature and severity of the pain.
TENS therapy is nevertheless a worthwhile alternative to medications when treating peripheral neuropathy symptoms, particularly with chronic pain.
Immunosuppressive and Immunomodulatory Therapies To Treat Peripheral Neuropathy
Surgery To Treat Peripheral Neuropathy
In severe cases of peripheral neuropathy, surgery may be the best treatment option. Surgical procedures can relieve the pressure on a damaged nerve. Those with tumors, a herniated disc in the neck or back, or nerve entrapment may be candidates for surgery (such as carpal tunnel syndrome).
As surgical technology continues to advance, an increasing number of peripheral neuropathy-related surgical procedures are minimally invasive. Minimally invasive surgery employs smaller incisions and precise, miniature instruments. Consequently, one can anticipate less scarring, less post operative pain, and a quicker recovery time.
Acupuncture To Treat Peripheral Neuropathy
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese technique for promoting natural healing and enhancing function. Depending on the location of pain or other symptoms, needles are inserted into the body at very specific points.
Acupuncture is believed to unblock the body's energy channels, also known as meridians. A more modern explanation is that needles can stimulate the nervous system when precisely positioned. In turn, this results in the release of chemicals (or a chain reaction of chemicals and hormones) that alter the perception of pain of the affected nerves and other symptoms.
Some acupuncture practitioners can actually use electrical stimulation instead of needles if you dislike needles. Another variation of this practice is acupressure. These techniques are particularly helpful with sensory neuropathy.
Mind/Body Practices To Treat Peripheral Neuropathy
Mind/body techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and tai chi are also treatment options for those struggling with peripheral neuropathy. Typically, these practices are used in conjunction with more conventional medicine.
In particular, these practices can lead to a more mindful experience of what is going on with you physically, mentally, and emotionally. This, in turn, can reduce stress and pain, promote relaxation, and improve your quality of life.
Some of the more physical mind/body practices, like yoga or tai chi, can also assist with flexibility and muscle tone.
Cognitive Treatment For Peripheral Neuropathy
Cognitive therapy is a type of psychotherapy in which negative thought patterns about the self and the world are challenged in order to modify undesirable behavior patterns or treat mood disorders like depression.
Individuals with disabilities and/or chronic health conditions may benefit from discussing their condition with a therapist. It is not always simple to deal with being unable to participate in the activities you enjoy. A psychotherapist can provide you with the tools and support necessary to investigate and manage your thoughts and emotions.
Summary
Peripheral neuropathy is damaged or diseased nerves of the peripheral nervous system. Peripheral neuropathy can be sensory, motor, or autonomic. Diabetes is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy, with peripheral and autonomic neuropathies being the most common forms of diabetic neuropathy. Autoimmune disorders can also cause peripheral neuropathy. The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include burning and tingling pain, motor neuropathy symptoms such muscle weakness, and other autonomic symptoms involving the digestive system, cardiovascular system, and the genitourinary system. The sooner peripheral neuropathy is diagnosed, the more effective treatment options will be at improving nerve health. Treatments of peripheral neuropathy include pain medication, neuropathic medication, transcutaneous nerve stimulation, immune system changes, and surgery. Other treatments include acupuncture, and various mind/body techniques as well as cognitive treatment.
The Enzyme
There is a particular enzyme in the body known as MMP-13, the inhibition of which has profound implications in the approach to neuropathy. We encourage to you click one of the buttons on this page to learn more.